Web API
This page provides detailed design information about the web API object and its configuration options.
Web APIs provide a way to expose eizen agentic platform data and services to outside systems.
Web APIs are created similarly to expression rules, but they differ in two key ways:
- They have an endpoint that external systems can call.
- Instead of relying on rule inputs, Web APIs accept values through query parameters, headers, a request body, or a combination of these.
Creating a Web API
To create an expression rule:
- In your application go to application view, select an application and either click on the application name or go to object view.
- Click the Create New drop down and select Web API.
- Configure the following properties:
- Name
- Click Create
After creating, it opens in a new dialog or window where you can configure the following properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Body | Used to send structured data from your system to an external system. It forms the main content of the HTTP request and typically contains information you want the server to create, update, or process. |
| Method | The HTTP method for your web API. Options include: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, and PATCH. |
| Name | The name of your web API. |
| Description | A short description about your web API. |
| Relative Path | Only the endpoint path used in platforms to append to base URLs. |
| Absolute Path | Full URL to call an API directly. |
| Headers | HTTP headers allow you to pass additional information with the response. |
| Query Parameters | key-value pair included at the end of a URL to send additional data to the server to filter, sort, or customize the data returned by an API. |
Web API Configuration – Key Points
When creating a Web API in the platform, the following configurations must be done carefully:
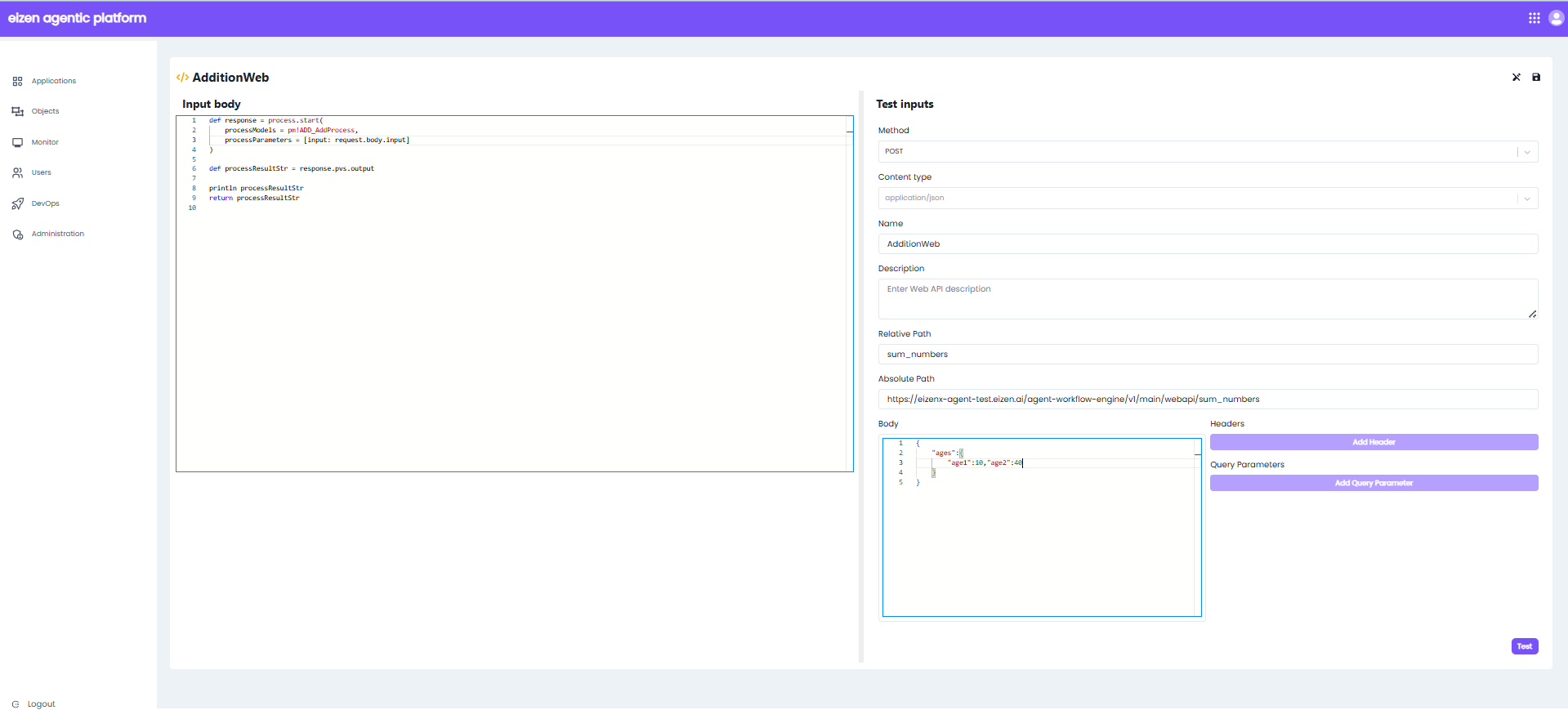
1. Relative Path
- The Relative Path is mandatory and defines the API endpoint that clients will call.
- This will be appended to the Absolute Path automatically.
2. Input Body
- The Input Body is defined by calling a Process Model.
- The call is done using the prefix
pm!, where: pm→ stands for Process Model.pm!ProcessModelName→ represents the process model that needs to be invoked.
3. pm! (Process Model Reference)
pm!allows linking a Process Model to the Web API.- This ensures that when the Web API is invoked, the respective Process Model executes with the given input.
4.Body Mapping
- The Body must be provided according to the defined:
- Input Body schema
- Rules in the process model
- Integration requirements